Projects
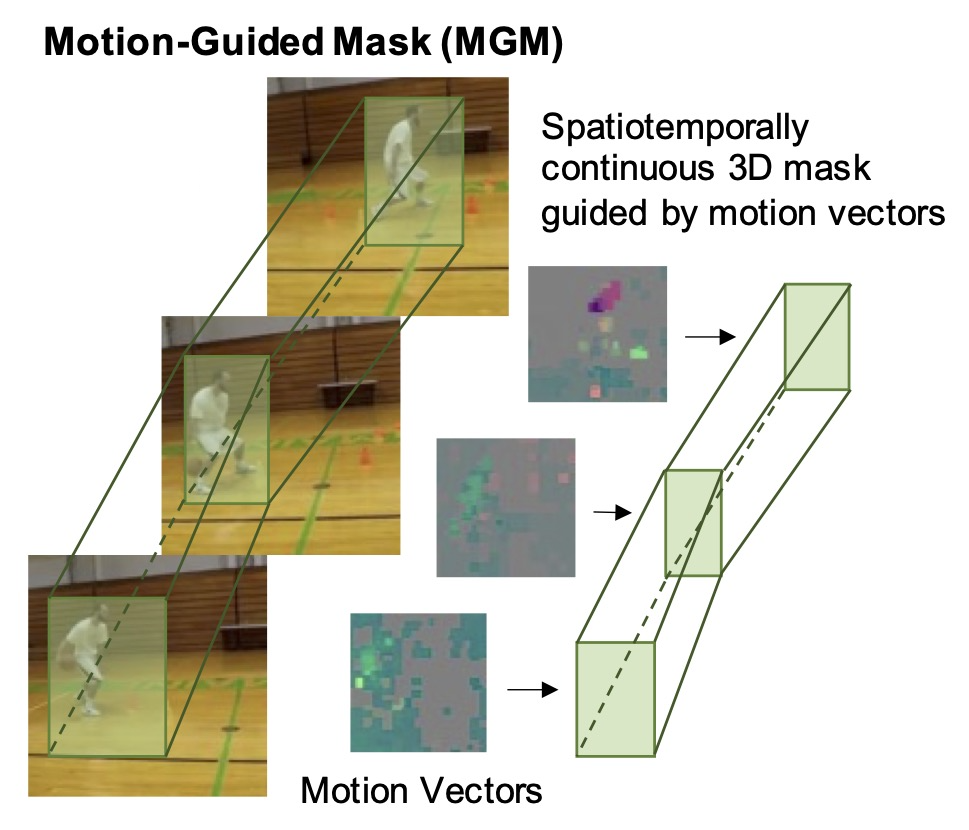
Motion-Guided Masking for Spatiotemporal Representation Learning
BERT popularized masked autoencoders for language modeling. Recent works have extended masked autoencoder to image and video domain by reconstructing randomly masked out image/video patches. These works show that MAE is a promising paradigm for scaling up self-supervised video pretraining. However, random masking assumes that information density is uniformly distributed.
In this work, we argue that masking saliency is key to elevating the efficacy of MAE for video. Specifically, we show that salient regions of video are tied to high motion. Thus, we propose to mask out the regions with highest motion. Vanilla video MAE equipped with our motion-guided masking (MGM) algorithm outperforms previous SOTA with up to 3x fewer pretraining epochs. We achieve state-of-the-art results for ViT-B on Kinetics-400 (81.7%) and Something-Something v2 (72.1%) and show that our MGM generalizes better to small datasets as well.
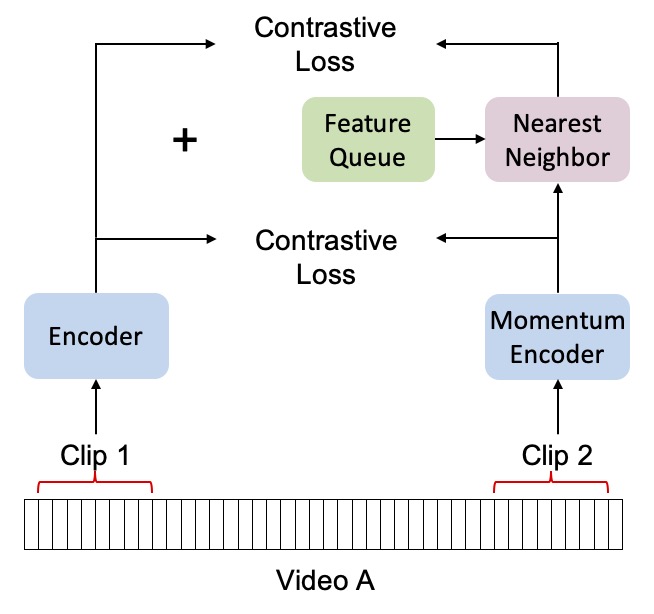
Nearest-Neighbor Inter-Intra Contrastive Learning from Unlabeled Videos
Popular contrastive learning methods for video such as CVRL sample non-overlapping positive subclips from within the same video. However, this intra-video sampling limits positive pair diversity because video similarity can transcend class boundaries. For instance, videos about skiing and snowboarding are more similar to each other than to videos about animals. Taking inspiration from NNCLR, we introduce global nearest-neighbor positive key sampling from a momentum queue to improve positive pair diversity. We show that this improves video representations for a variety of downstream video recognition and retrieval tasks, even in zero-shot settings.
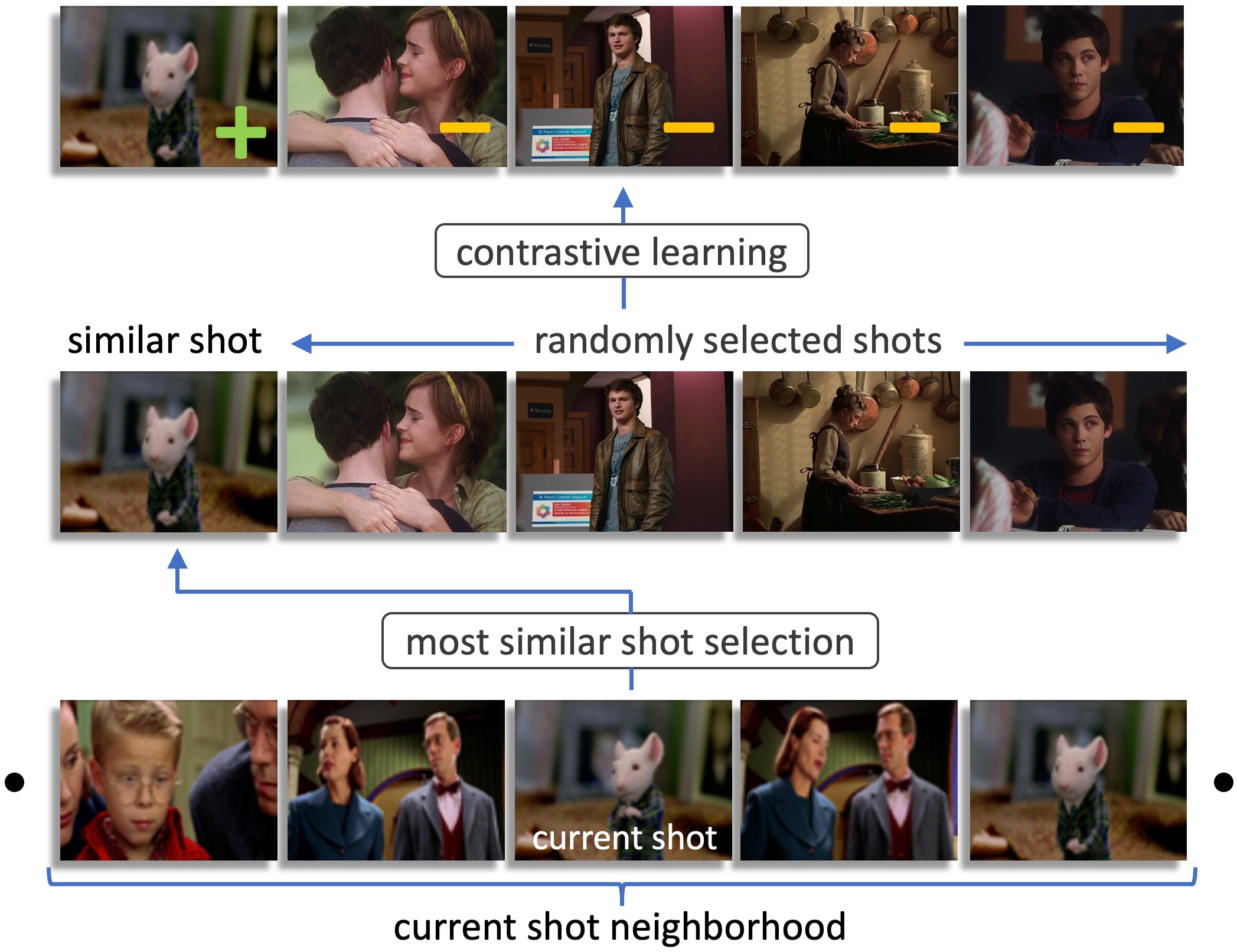
Shot Contrastive Self-Supervised Learning for Scene Boundary Detection
Scenes are critical to long-form video understanding as they delineate semantic progression. Localization of scenes is an important problem that is foundational to higher-level tasks in video understanding. Movies are particularly interesting as they are longer, more semantically complicated, and more visually challenging compared to most video datasets which contain clean short videos.
We present a novel pretext task that encourages the model to project embeddings from nearest neighboring shots to be closer in the embedding space than randomly sampled negative shots. Our pretext task exploits invariance in the shot-based scene structure of movies to learn a better representation via self-supervised contrastive learning. Using this representation, we are able to beat previous state-of-art on MovieNet by 6 AP points while running 7x faster and using 9x fewer parameters. In addition, we present a new dataset for a downstream application called advertisement cuepoint insertion.
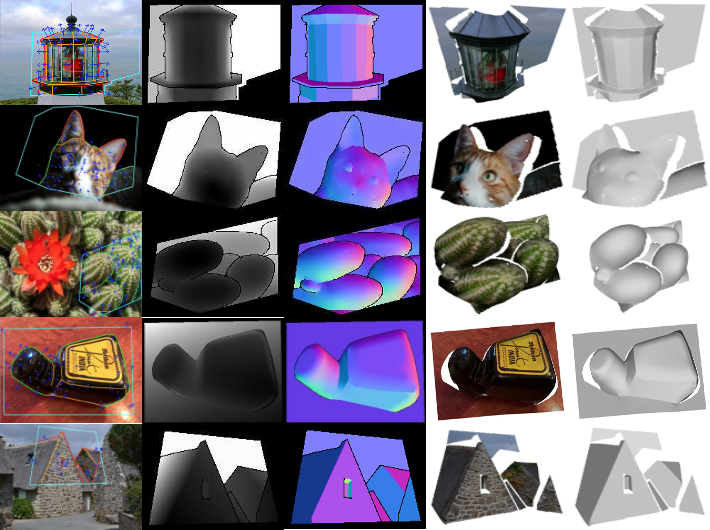
OASIS: A Large-Scale Dataset for Single-Image 3D in the Wild
Lack of high-quality, diverse, and large-scale data impedes research in many fields, including single-image 3D vision. For my senior thesis, I helped create OASIS, a large-scale dataset for single-image 3D in the wild. I implemented a pipeline for crowdsourcing dense pixel-wise 3D ground truths from sparse annotations, and quality control mechanisms to ensure annotation consistency.
I also trained state-of-art deep learning models to benchmark OASIS for monocular surface normal estimation and planar semantic segmentation, and evaluate cross-dataset generalization. I provided the baseline for fold and occlusion boundary detection. The dataset improves performance in multiple visual tasks, and also introduces new tasks for research.
This work was accepted to CVPR 2020 and advised by Professor Jia Deng.
TigerTexts | Spring 2018
Finding coursebook info for Princeton students is unnecessarily difficult. I built a web app that consolidates Princeton coursebook pricing from multiple sources, and offers third-party seller options, thus providing the most complete information on cheap textbooks. Built in Express.js, React, Redux, Python, and MongoDB.
Lyff | PennApps Fall 2017
We built a voice bot that users can call to order a Lyft ride. This is useful where Internet and/or cellular data is inaccesible (which can happen even in urban areas, from personal experience). We won the “Best use of Vonage/Nexmo API” prize. The following APIs were used: Nexmo for the voice bot, Amazon Lex/Lambda for voice processing and parsing, Google Maps API to sanitize locations, Lyft API for making Lyft calls. Press received:
1. Nexmo Blog
Princeton University Science Olympiad | Fall 2016
In Fall 2016, I co-founded a tournament that hosts 800 high school students from around the nation each year. I led a team of 8 undergrad students and 120 volunteers in the execution of 23 competition events, and raised a budget of $10,000. In 2017, we became the first college-run tournament nationwide to waive registration fees. I developed the static website in HTML/CSS/Javascript.
We have received the following press:
1. Scientific American
2. Princeton University
HackPrinceton | Fall 2016 - Spring 2018
HackPrinceton is Princeton’s biannual student-run hackathon which hosts 1,100 students per year. As co-director From Fall 2017-Spring 2018, I led a team of 30 undergraduate organizers and combined budget of $150,000.
From Fall 2016-Spring 2017, I was an organizer and coordinated bus routes, workshops, prizes, and mentorship. Below is a sample of the press we have received:
1. Business Insider
2. Princeton School of Engineering
3. Princeton Entreneurship Council
UBiT2 | Summer 2016
I worked with Dr. Jean Fan to develop an open-source web application for client-side RNA-seq and qPCR data analysis. All computation and data visualization is done client-side, thus providing a secure and fast environment for bioinformatics that involves no server. Built in HTML, CSS, and Javascript.
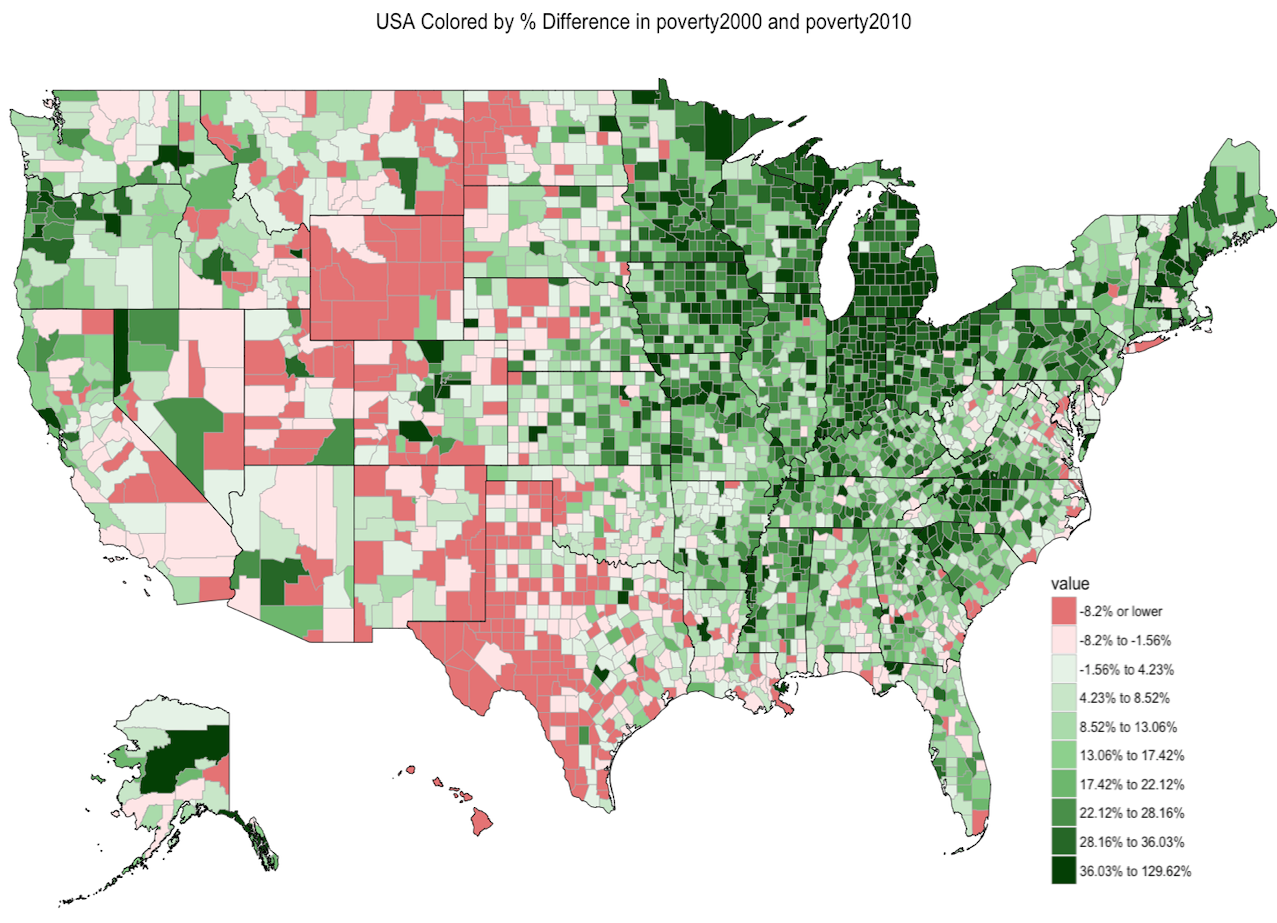
Claims-Wide Association Study | Summer 2016
I worked with Prof. Isaac Kohane and Dr. Arjun Manrai to develope a new association study called “claims-wide association study (CWAS)” - like genome-wide association studies (GWAS), but for insurance claims. I built a data visualization tool for plotting heatmaps of the USA from parsed AETNA insurance claims, at multiple levels of geographic specificity (zipcode, county, state, regional). Built in R, MySQL, and the Shiny web framework.